
Aphasia is a disorder that affects how you communicate. It can impact your speech, as well as the way you write and understand both spoken and written language. Aphasia usually happens suddenly after a stroke or a head injury. But it can also come on gradually from a slow-growing brain tumor or a disease that causes progressive, permanent damage (degenerative). The severity of aphasia depends on a number of things, including the cause and the extent of the brain damage. The main treatment for aphasia involves treating the condition that causes it, as well as speech and language therapy. The person with aphasia relearns and practices language skills and learns to use other ways to communicate. Family members often participate in the process, helping the person communicate.
Symptoms
Aphasia is a symptom of some other condition, such as a stroke or a brain tumor.
A person with aphasia may:

- Speak in short or incomplete sentences
- Speak in short or incomplete sentences
- Substitute one word for another or one sound for another
- Speak unrecognizable words
- Have difficulty finding words
- Not understand other people's conversation
- Not understand what they read
- Write sentences that don't make sense
Types
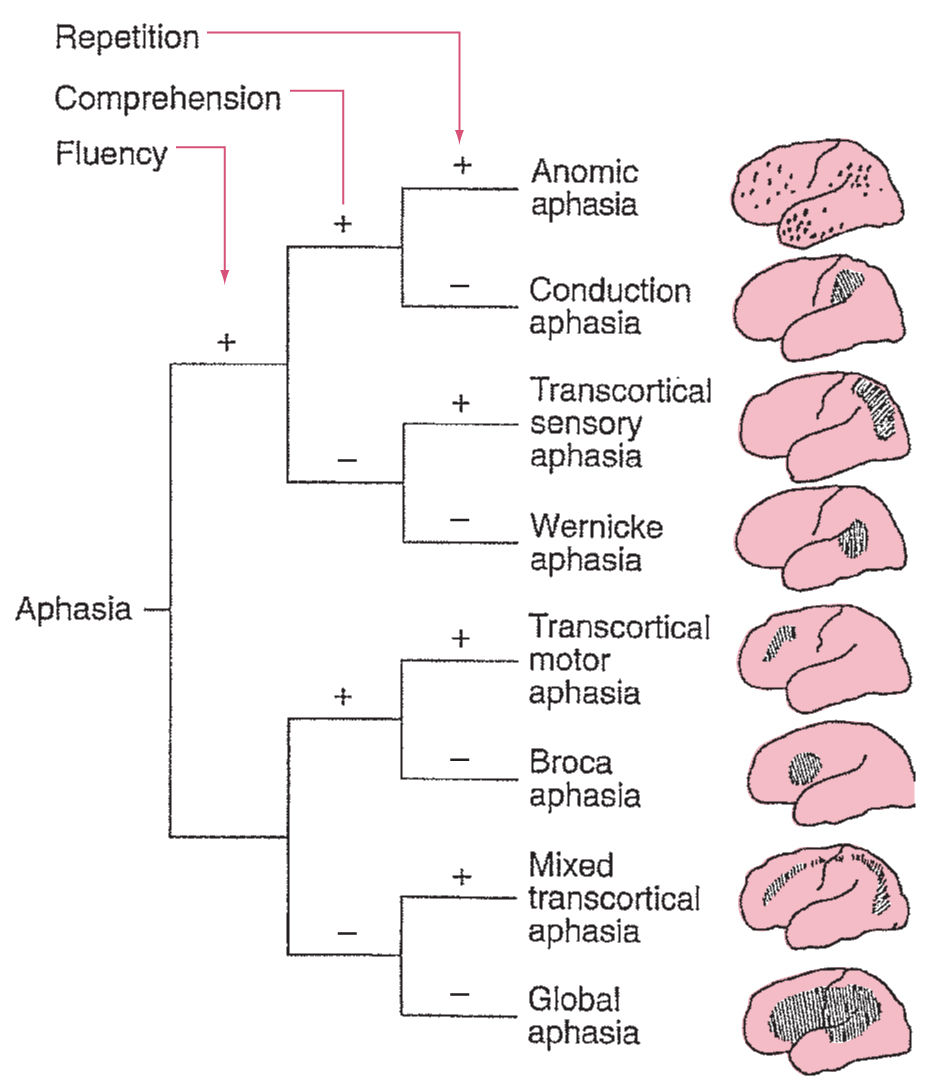
- People with aphasia may have different strengths and weaknesses in their speech patterns. Sometimes these patterns are labeled as different types of aphasia, including:
- Broca's aphasia
- Wernicke aphasia
- Transcortical aphasia
- Conduction aphasia
- Mixed aphasia
- Global aphasia
- These patterns describe how well the person can understand what others say. They also describe how easy it is for the person to speak or to correctly repeat what someone else says.
- Logopenic aphasia
- Semantic aphasia
- Agrammatism
- Many people with aphasia have patterns of speech difficulty that don't match these types. It may help to consider that each person with aphasia has unique symptoms, strengths and weaknesses rather than trying to label a particular type of aphasia.
Call MVM Vākśravaṇa Clinic at 080-69956566 for more information or to schedule an appointment.
